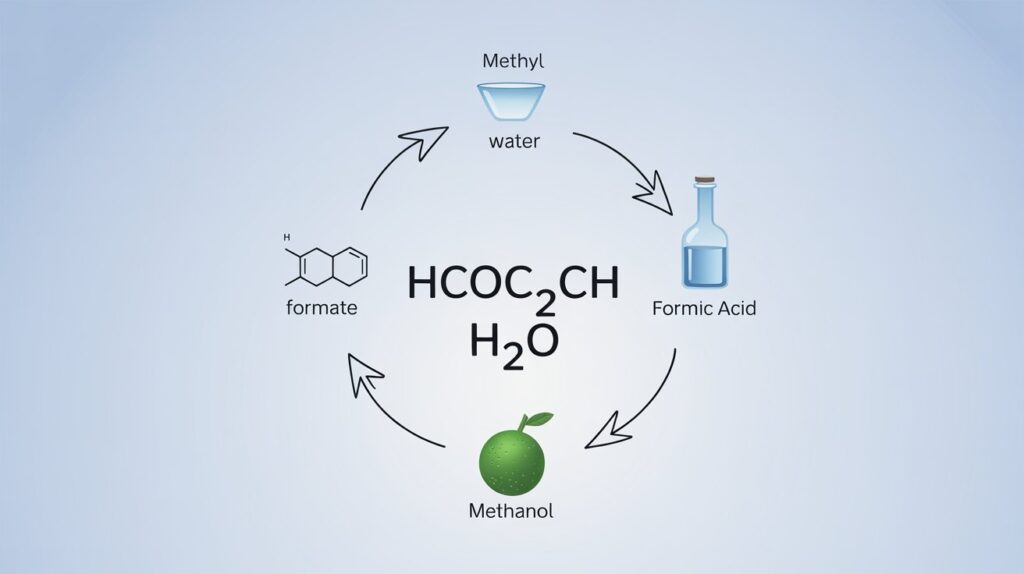
Chemical Reaction: Ester Hydrolysis of HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O
HCOOCH₃
Methyl Formate
H₂O
Water
HCOOH
Formic Acid
CH₃OH
Methanol
At first glance, “HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O” might appear as a cryptic string of chemical symbols. However, this notation encapsulates a fascinating interplay between formic acid derivatives, methylene groups, and water molecules. Understanding this molecular combination opens doors to various chemical reactions and applications in organic chemistry.
Table: Detailed Biography of “HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O”
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Chemical Notation | HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O |
| Full Components | Methyl formate (HCOOCH₃), methylene group (CH₂), water (H₂O) |
| Reaction Types | Ester Hydrolysis, Alkene Hydration |
| Key Reactions Involved | – Ester Hydrolysis: HCOOCH₃ + H₂O → HCOOH + CH₃OH – Alkene Hydration: Water reacts with alkenes to form alcohols |
| Applications | Pharmaceuticals, Polymer Chemistry, Environmental Chemistry, Biodiesel Production |
| Significance | Key for organic synthesis, biodegradation, and industrial chemistry |
| Importance of Water | Water is a key reactant in ester hydrolysis and alkene hydration reactions |
| Industries Impacted | Drug manufacturing, plastic polymers, environmental sustainability |
| Synthesis Pathway | Esterification (Formic acid + Methanol), Incorporation of CH₂, Hydrolysis with water |
| Real-World Use | Used in synthetic reactions, plastic degradation, drug synthesis |
| Synonyms and Variations | Methyl formate, Ester hydrolysis, Alkene hydration |
| Recent Research (2024-2025) | Studies focus on sustainable ester hydrolysis and alkene hydration methods in green chemistry and drug development |
What Is HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O?
Breaking down the components:
- HCOOCH: This represents an ester group, specifically methyl formate (HCOOCH₃), formed from formic acid and methanol.
- CH₂: A methylene group, a two-carbon unit (-CH₂-), often involved in organic reactions.
- H₂O: Water, a universal solvent and reactant in numerous chemical processes.
Together, these components suggest a molecular structure where methyl formate interacts with a methylene group and water, potentially undergoing reactions like ester hydrolysis or alkene hydration.
How Does HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O React?
1. Ester Hydrolysis
Ester hydrolysis is a fundamental reaction where an ester reacts with water to produce an alcohol and an acid. In the case of methyl formate:
HCOOCH₃ + H₂O → HCOOH + CH₃OH
This reaction is crucial in various industrial processes, including the production of formic acid and methanol. Under acidic or basic conditions, the ester bond is broken, leading to the formation of the respective products.
2. Alkene Hydration
While “HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O” doesn’t directly represent an alkene, the notation hints at the involvement of water in reactions with alkenes. In organic chemistry, the addition of water to an alkene (hydration) results in the formation of an alcohol. This process is vital in producing various alcohols used in industrial applications.
Real-World Applications of HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O
1. Pharmaceuticals
Methyl formate and its derivatives play a role in the synthesis of various pharmaceutical compounds. Understanding the reactions involving HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O aids in designing efficient synthetic pathways for drug development.
2. Polymer Chemistry
The methylene group (CH₂) is a building block in polymer chemistry. Reactions involving HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O can lead to the formation of polymers with specific properties, useful in creating materials with desired characteristics.
3. Environmental Chemistry
Ester hydrolysis reactions, such as those involving HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O, are significant in environmental chemistry. They contribute to the breakdown of esters in natural systems, impacting processes like biodegradation and the cycling of organic compounds.
How Is HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O Synthesized?
The synthesis of HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O involves several steps:
- Esterification: Formic acid reacts with methanol in the presence of a catalyst to form methyl formate (HCOOCH₃).
- Incorporation of Methylene Group: The methylene group (CH₂) is introduced into the reaction, potentially through various organic reactions.
- Hydrolysis: Water is added to the system, leading to the hydrolysis of the ester bond, producing formic acid and methanol.
Why Should You Care About HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O?
Understanding the reactions and applications of HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O provides insights into fundamental organic chemistry processes. These reactions are not just theoretical; they have practical implications in industries ranging from pharmaceuticals to environmental science.
Key Takeaways
- Ester Hydrolysis: Methyl formate reacts with water to produce formic acid and methanol.
- Alkene Hydration: Water addition to alkenes forms alcohols, a vital process in organic synthesis.
- Applications: Reactions involving HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O are crucial in pharmaceuticals, polymer chemistry, and environmental processes.
- Synthesis Pathways: The compound is synthesized through esterification, incorporation of methylene groups, and hydrolysis.
Further Reading
For more detailed information on ester hydrolysis and alkene hydration, consider exploring the following resources:
These resources delve deeper into the mechanisms and applications of these fundamental reactions in organic chemistry.
In conclusion, “HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O” represents more than just a chemical formula; it embodies essential reactions and applications in organic chemistry. By understanding its components and reactions, we gain valuable insights into processes that impact various industries and scientific fields.